life is too short for a diary
On This Page
Fri 23 Oct 2020
Export DynamoDB Table to S3 Bucket Using Lambda Function
Tags: aws lambda function dynamodb s3
Dynamodb is a great NoSQL service by AWS. Often it’s required to export data from the dynamodb table .
First, let us review our use case. Our lambda function will read from table from dynamodb and export JSON to s3.
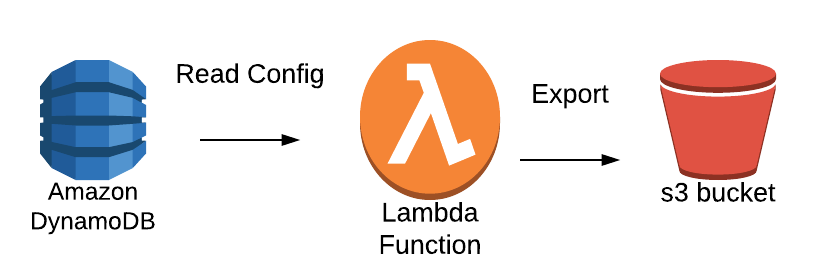 |
Using boto3 resource
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| import json | |
| import traceback | |
| import boto3 | |
| def lambda_handler(event, context): | |
| """ | |
| Export Dynamodb to s3 (JSON) | |
| """ | |
| statusCode = 200 | |
| statusMessage = 'Success' | |
| try: | |
| # parse the payload | |
| tableName = event['tableName'] | |
| s3_bucket = event['s3_bucket'] | |
| s3_object = event['s3_object'] | |
| filename = event['filename'] | |
| # scan the dynamodb | |
| dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb') | |
| table = dynamodb.Table(tableName) | |
| response = table.scan() | |
| data = response['Items'] | |
| # maximum data set limit is 1MB | |
| # so we need to have this additional step | |
| while 'LastEvaluatedKey' in response: | |
| response = dynamodb.scan( | |
| TableName=tableName, | |
| Select='ALL_ATTRIBUTES', | |
| ExclusiveStartKey=response['LastEvaluatedKey']) | |
| data.extend(response['Items']) | |
| # export JSON to s3 bucket | |
| s3 = boto3.resource('s3') | |
| s3.Object(s3_object, s3_object + filename).put(Body=json.dumps(data)) | |
| except Exception as e: | |
| statusCode = 400 | |
| statusMessage = traceback.format_exc() | |
| return { | |
| "statusCode": statusCode, | |
| "status": statusMessage | |
| } |
We can create a payload to test our lambda function
{
"TableName": "DynamoDB_Table_name",
"s3_bucket": "s3_bucket_name",
"s3_object": "s3_object_name",
"filename": "output.json"
}
However, sometimes we might encounter errors for certain values in DynamoDB.
TypeError: Object of type Decimal is not JSON serializable.
We can use a JSONEncoder class to update our lamda function.
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| import json | |
| import traceback | |
| import boto3 | |
| from collections.abc import Mapping, Iterable | |
| from decimal import Decimal | |
| class DecimalEncoder(json.JSONEncoder): | |
| def encode(self, obj): | |
| if isinstance(obj, Mapping): | |
| return '{' + ', '.join(f'{self.encode(k)}: {self.encode(v)}' for (k, v) in obj.items()) + '}' | |
| elif isinstance(obj, Iterable) and (not isinstance(obj, str)): | |
| return '[' + ', '.join(map(self.encode, obj)) + ']' | |
| elif isinstance(obj, Decimal): | |
| return f'{obj.normalize():f}' # using normalize() gets rid of trailing 0s, using ':f' prevents scientific notation | |
| else: | |
| print(obj) | |
| return super().encode(obj) | |
| def lambda_handler(event, context): | |
| """ | |
| Export Dynamodb to s3 (JSON) | |
| """ | |
| statusCode = 200 | |
| statusMessage = 'Success' | |
| try: | |
| # parse the payload | |
| tableName = event['tableName'] | |
| s3_bucket = event['s3_bucket'] | |
| s3_object = event['s3_object'] | |
| filename = event['filename'] | |
| # scan the dynamodb | |
| dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb') | |
| table = dynamodb.Table(tableName) | |
| response = table.scan() | |
| data = response['Items'] | |
| # maximum data set limit is 1MB | |
| # so we need to have this additional step | |
| while 'LastEvaluatedKey' in response: | |
| response = dynamodb.scan( | |
| TableName=tableName, | |
| Select='ALL_ATTRIBUTES', | |
| ExclusiveStartKey=response['LastEvaluatedKey']) | |
| data.extend(response['Items']) | |
| # export JSON to s3 bucket | |
| s3 = boto3.resource('s3') | |
| body = json.dumps(data, cls=DecimalEncoder) | |
| s3.Object(s3_bucket, s3_object + filename).put(Body=json.dumps(data)) | |
| except Exception as e: | |
| statusCode = 400 | |
| statusMessage = traceback.format_exc() | |
| return { | |
| "statusCode": statusCode, | |
| "status": statusMessage | |
| } |
Using boto3 client
Another way to export data is to use boto3 client. It’s a low level AWS services.
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| import json | |
| import traceback | |
| import boto3 | |
| def get_data(table_name, client): | |
| """ | |
| Get data from DyanamoDB | |
| """ | |
| results = [] | |
| last_evaluated_key = None | |
| while True: | |
| if last_evaluated_key: | |
| response = client.scan( | |
| TableName=table_name, | |
| ExclusiveStartKey=last_evaluated_key | |
| ) | |
| else: | |
| response = client.scan(TableName=table_name) | |
| last_evaluated_key = response.get('LastEvaluatedKey') | |
| results.extend(response['Items']) | |
| if not last_evaluated_key: | |
| break | |
| return results | |
| def lambda_handler(event, context): | |
| """ | |
| Export Dynamodb to s3 (JSON) | |
| """ | |
| statusCode = 200 | |
| statusMessage = 'Success' | |
| try: | |
| # parse the payload | |
| tableName = event['tableName'] | |
| s3_bucket = event['s3_bucket'] | |
| s3_object = event['s3_object'] | |
| filename = event['filename'] | |
| # scan the dynamodb | |
| dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb') | |
| table = dynamodb.Table(tableName) | |
| client = boto3.client('dynamodb') | |
| data = get_data(tableName, client) | |
| # export JSON to s3 bucket | |
| s3 = boto3.resource('s3') | |
| s3.Object(s3_bucket, s3_object + filename).put(Body=json.dumps(data)) | |
| except Exception as e: | |
| statusCode = 400 | |
| statusMessage = traceback.format_exc() | |
| return { | |
| "statusCode": statusCode, | |
| "status": statusMessage | |
| } |
However boto3 client will generates dynamodb JSON. A simple python script to convert it back to normalized JSON using dynamodb_json library.
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| import time | |
| import uuid | |
| from datetime import datetime | |
| from decimal import Decimal | |
| from dynamodb_json import json_util as json2 | |
| import json | |
| import sys | |
| filename = sys.argv[1] | |
| output = sys.argv[2] | |
| with open(filename) as f: | |
| data = json.load(f) | |
| data_new = json2.load(data) | |
| with open(output, 'w') as outfile: | |
| json.dump(data_new, outfile) |